The Minds Behind Libertarianism: Mises, Rothbard, and Hayek
Delve into the foundational theories of Libertarianism through the perspectives of Ludwig von Mises, Murray Rothbard, and Friedrich Hayek. This article examines their key ideas, contributions, and impact on modern libertarian philosophy.
Introduction
The roots of libertarianism can be traced back to the groundbreaking ideas of three influential thinkers: Ludwig von Mises, Murray Rothbard, and Friedrich Hayek. Their contributions to economics, philosophy, and political theory have shaped the core principles of modern libertarian thought. Let's delve into their ideas to understand what drives libertarianism today.
Ludwig von Mises
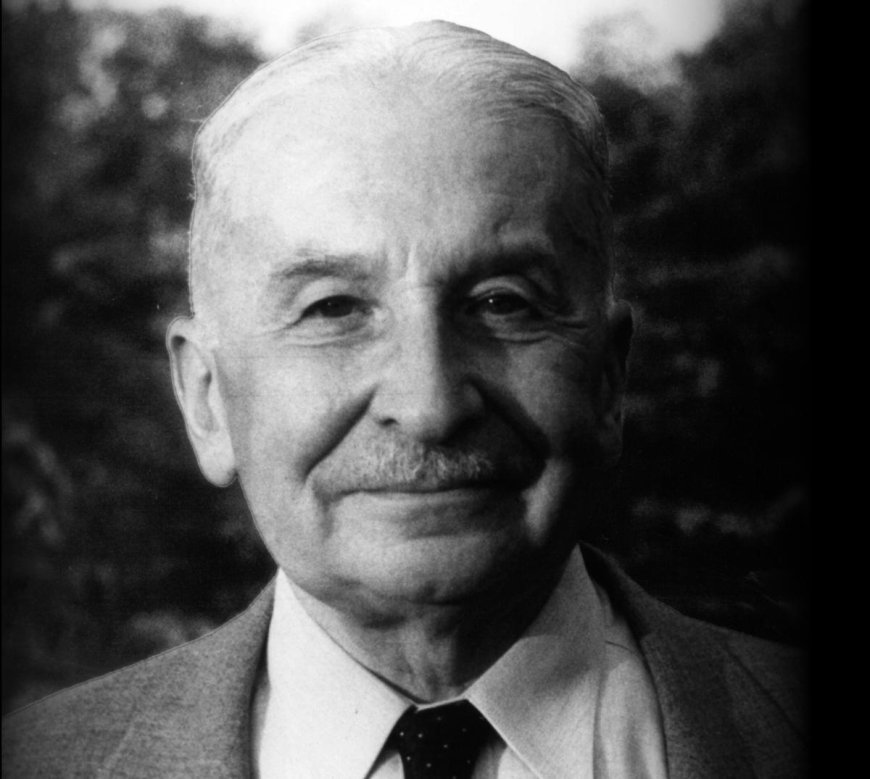

Ludwig von Mises, a giant in the field of economics, was born in 1881. His work, including classics like "Human Action" and "Socialism," remains a cornerstone for those who advocate for free markets and limited government intervention.
Economic Calculation Problem
Mises is well-known for his Economic Calculation Problem, which argues that socialism and central planning are doomed to fail because they can't use price signals to allocate resources efficiently. Without these signals, central planners can't avoid waste and inefficiency, strengthening the libertarian argument for free markets.
Human Action and Praxeology
Mises introduced praxeology, the study of human action based on the idea that people act with purpose. This approach highlights how individual choices shape economic outcomes, aligning with the libertarian emphasis on personal freedom and responsibility.
Murray Rothbard
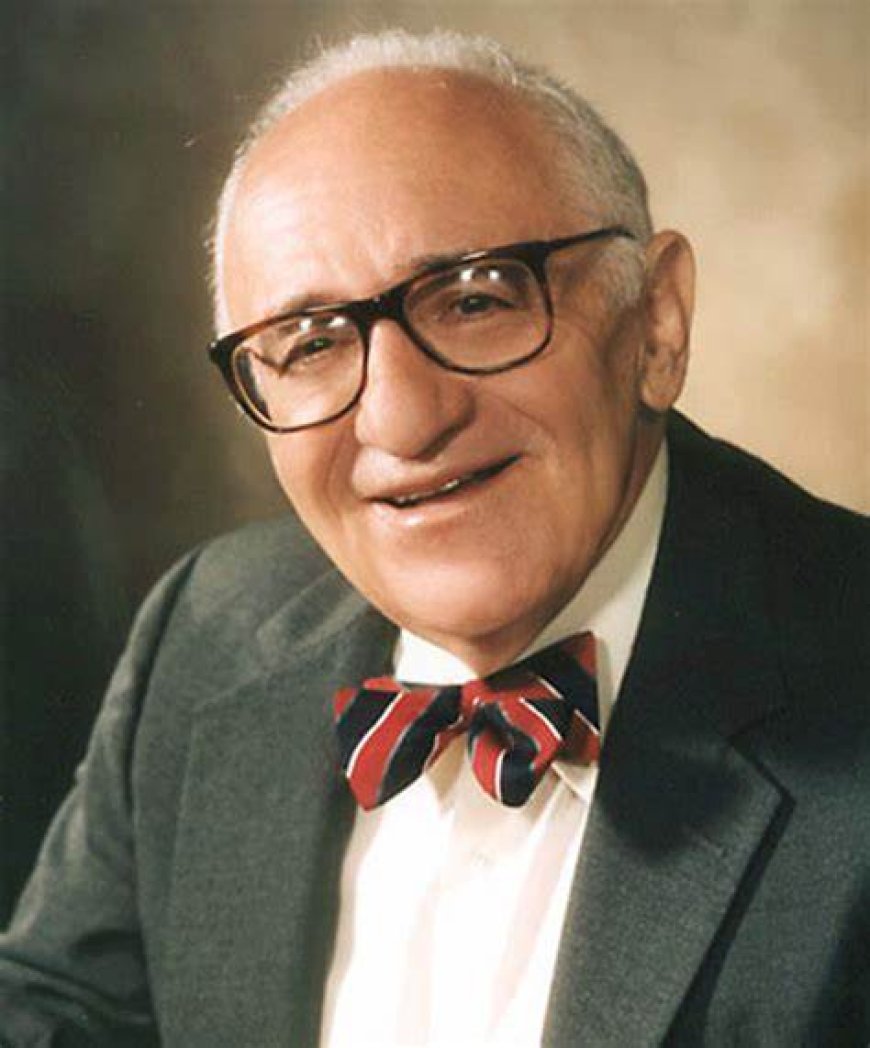

Murray Rothbard, a student of Mises born in 1926, took his mentor's ideas further and became a leading voice in the libertarian movement. His influential works, such as "Man, Economy, and State" and "For a New Liberty," are essential readings for libertarians.
Anarcho-Capitalism
Rothbard is best known for his vision of anarcho-capitalism, where all services, including security and justice, are provided by private individuals and businesses rather than the state. He argued that the state is inherently coercive and that voluntary, market-based solutions are better.
Ethics of Liberty
In "The Ethics of Liberty," Rothbard outlines a moral framework based on natural rights and the non-aggression principle. He believes individuals have the right to do anything as long as they don't infringe on others' rights, a key tenet of libertarian philosophy.
Friedrich Hayek
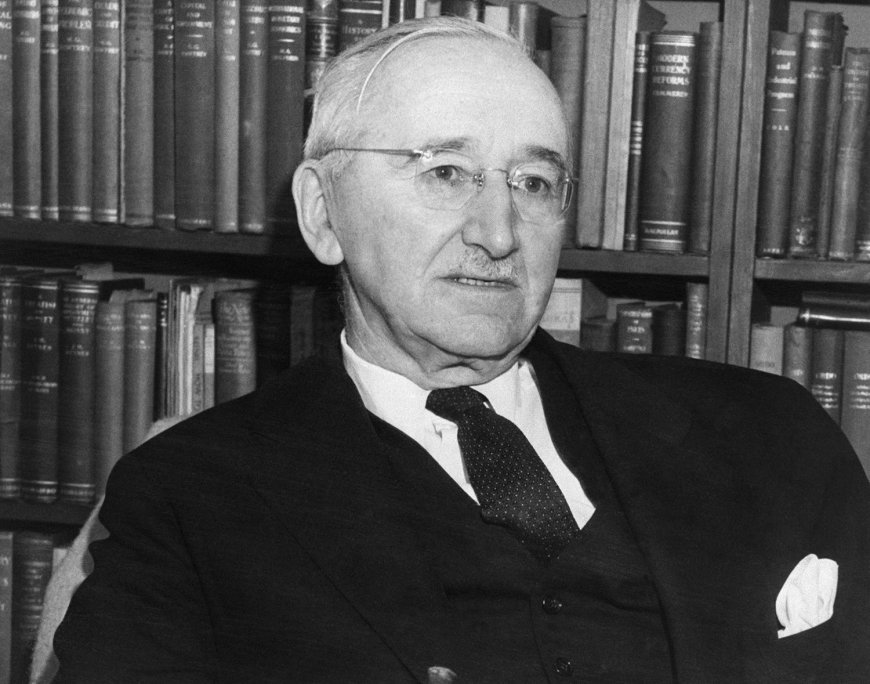

Friedrich Hayek, another influential Austrian economist born in 1899, made significant contributions to libertarian thought, especially regarding the limits of knowledge and the spontaneous order of markets. His seminal works include "The Road to Serfdom" and "The Constitution of Liberty."
The Knowledge Problem
Hayek's Knowledge Problem addresses the challenges central planners face in gathering and using all the information needed to make efficient economic decisions. He argued that only decentralized markets, through the price mechanism, can effectively utilize dispersed knowledge.
Spontaneous Order
Hayek introduced the concept of spontaneous order, where organization and order naturally arise from individuals' actions without central direction. This idea supports the libertarian belief in the power of free markets and voluntary interactions to create a prosperous society.
Comparative Analysis
While Mises, Rothbard, and Hayek share a commitment to individual liberty and free markets, their approaches differ. Mises focused on praxeology and the economic calculation problem, Rothbard emphasized anarcho-capitalism and natural rights, and Hayek highlighted the knowledge problem and spontaneous order. Together, their ideas provide a comprehensive foundation for libertarian thought.
Impact on Modern Libertarianism
The ideas of Mises, Rothbard, and Hayek have profoundly influenced modern libertarianism. Their arguments for limited government, free markets, and individual liberty continue to shape policy debates and inspire libertarian scholars and activists.
Criticisms and Counterarguments
Critics argue that libertarianism's focus on free markets can lead to inequality and that its minimal government approach may neglect necessary public goods. Libertarians respond by pointing out the inefficiencies and coercion in government intervention, advocating for voluntary solutions and charitable efforts to address social issues.
Real-World Examples
Several regions have successfully applied libertarian principles. For instance, Hong Kong's free-market policies have led to significant economic growth and prosperity. Similarly, New Zealand's deregulation in the 1980s brought about notable economic improvements.
Conclusion
The contributions of Ludwig von Mises, Murray Rothbard, and Friedrich Hayek to libertarianism are invaluable. Their insights into economics, ethics, and social organization offer a robust framework for understanding and advocating for a free society. Exploring their works further can deepen one's appreciation of libertarian principles and their practical applications.
FAQs
-
What is the core belief of libertarianism? Libertarianism centers on maximizing individual freedom and minimizing government intervention in personal and economic matters.
-
How do Mises, Rothbard, and Hayek differ in their approaches? Mises focused on praxeology and the economic calculation problem, Rothbard on anarcho-capitalism and natural rights, and Hayek on the knowledge problem and spontaneous order.
-
Can libertarianism work in practice? Yes, examples like Hong Kong and New Zealand show that libertarian principles can lead to economic growth and prosperity.
-
What are the criticisms of libertarianism? Critics argue it can lead to inequality and overlook public goods. Libertarians counter that government intervention is inefficient and coercive, and voluntary solutions are preferable.
-
Why are Mises, Rothbard, and Hayek important to libertarianism? Their ideas form the intellectual foundation of modern libertarianism, offering comprehensive arguments for limited government, free markets, and individual liberty.
What's Your Reaction?


















































